Clone
After creating a repository, you can work directly in the Harness Code UI or you can clone your repo to your local machine and use your favorite IDE.
Clone over HTTPS
-
When viewing a repository in Harness Code, go to Files and select Clone.
-
If this is the first time you've cloned this repository, select Generate Clone Credentials, and then copy the Password (API Token) and store it somewhere secure. Clone credentials are only shown once.
When you select Generate Clone Credentials, Harness Code automatically creates an API token in your user profile.
warningTokens carry many privileges; treat your user tokens as passwords and store them securely.
-
Copy the Git clone URL shown on the Clone dropdown, and use it to clone your repository through command line Git or with your preferred Git GUI tool.
When cloning the repository, you will be prompted for your Harness user name and the API token, which were shown when you generated clone credentials.
-
Once cloned locally, you can work with your Harness Code repository as you would with other Git repositories, by creating commits, pushing to the remote, pulling changes, and more.
Clone over SSH
You can clone any Harness Code Repository using SSH if you prefer key-based authentication.
This feature is behind the CODE_SSH_ENABLED feature flag. To enable it, contact Harness Support.
Prerequisites
- You must have an SSH key pair on your local machine. To check:
ls ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
If it does not exist, generate one:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
Press Enter to accept the defaults.
- Add Your SSH Key to Harness
-
In the bottom-left corner of the Harness UI, click your Profile icon.
-
Select + SSH Key.
-
Enter a name for the key and paste your public SSH key.
-
Click Save.
Steps to Clone
- In Harness, navigate to the repository you want to clone and copy its SSH URL.
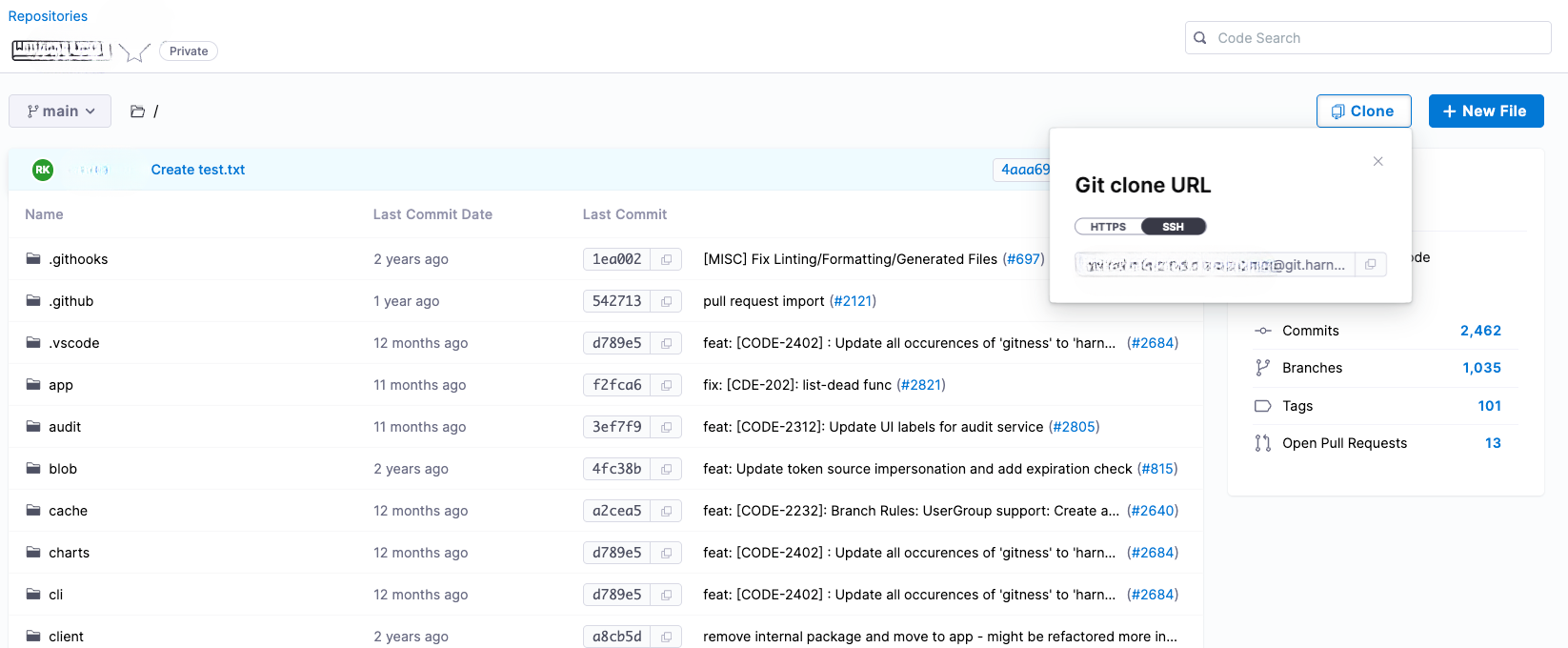
The format will look like this:
<USER_ID>@git.harness.io:<USER_ID>/<ACCOUNT_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/<REPO_NAME>.git
- From your terminal, run:
git clone '<USER_ID>@git.harness.io:<USER_ID>/<ACCOUNT_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/<REPO_NAME>.git'
Example:
git clone 'AB12CD34EF56@git.harness.io:AB12CD34EF56/CODE/CODE/sample-app.git'
- Change into the cloned repository directory and verify the remote:
cd sample-app
git remote -v
- You should see the SSH URL listed as
origin.
Partial and Shallow Clone Support (Filtering in git clone)
Harness Code Repository supports filtering during git clone operations to improve performance, especially for large monorepos or multi-service repositories.
When cloning large repositories, the default behavior of Git is to download the entire commit history and all associated blobs/trees, resulting in significant bandwidth usage and long clone times. To address this, you can use Git’s built-in partial clone and shallow clone features with Harness-hosted repositories.
You can use the --filter flag with git clone against Harness Code Repositories:
git clone --filter=blob:none <REPO_URL>
Refer to the official Git documentation on --filter.
This reduces the amount of data transferred during clone by excluding blobs initially. They are fetched lazily only when needed.
You can also combine this with shallow clone options:
git clone --depth=1 --filter=blob:none <REPO_URL>
Make sure your Git version is 2.19 or later to use filtering options.